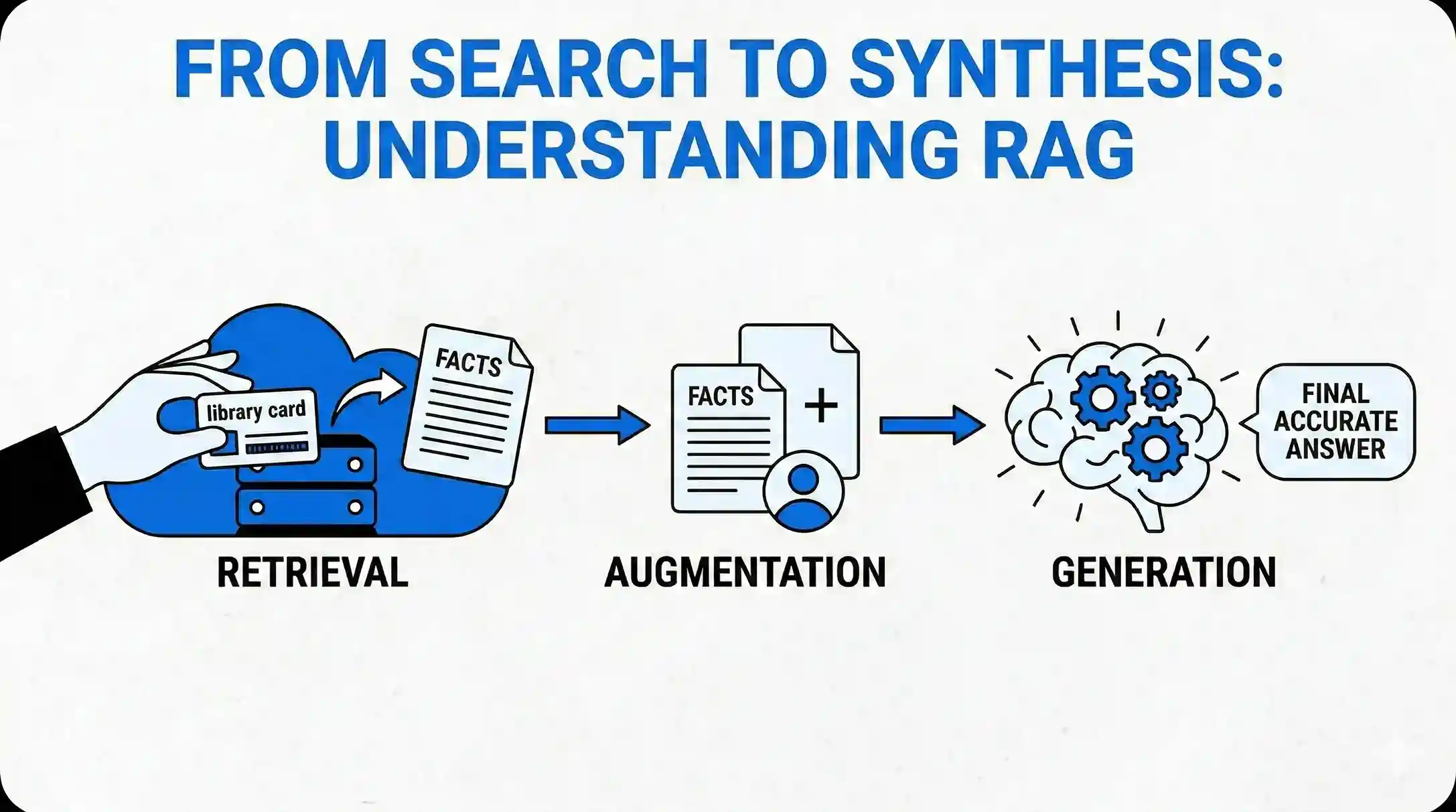
LLMs are advanced artificial intelligence systems that have the remarkable ability to understand and generate human language. They are trained on extensive collections of text data, enabling them to grasp the intricacies of language and produce responses that are not only coherent but also contextually relevant. The advent of LLMs has been a game-changer in the field of technology. They serve as the backbone for various applications that require natural language processing, from virtual assistants that can engage in conversation to systems that can create content indistinguishable from that written by humans.
How Do LLMs Work?
At the heart of LLMs lies the transformer architecture, a breakthrough in machine learning that allows these models to focus on different parts of a sentence to understand its meaning fully. This architecture is adept at handling long sequences of text, which is essential for tasks that require a deep understanding of language, such as translating languages, summarizing information, and generating text.
Types of LLMs and their uses in businesses:
Autoregressive Models:
These models predict the next part of the text based on the previous content. GPT-3 and GPT-4 are prime examples, known for their ability to generate human-like text. They can be used for creative writing, generating code, and even engaging in dialogue with users.
Use Case: A company can use GPT-3 to automate responses to customer inquiries on their website, providing instant, human-like interaction that improves customer service and engagement.
Autoencoding Models:
Models like BERT and T5 BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) are designed to understand the context of a word within a sentence, making it great for tasks that require a deep understanding of language, such as sentiment analysis and content categorization. T5 (Text-to-Text Transfer Transformer) takes this further by converting all NLP problems into a text-to-text format, which simplifies the process of applying the model to a variety of tasks.
Use Case: An online retailer could use BERT to analyze customer reviews and feedback, categorizing comments by sentiment and identifying key areas for improvement.
Multimodal Models:
A multimodal model like CLIP (Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining) can understand and generate text and images together. This capability is particularly useful for tasks that require bridging the gap between visual content and language, such as generating image captions or conducting visual searches.
Use Case: A travel agency might implement CLIP to create descriptive captions for images on their website, enhancing the user experience for clients seeking vacation inspiration.
Zero-Shot Models:
Zero-shot learning models like GPT-3 can perform tasks without any prior examples, based on their extensive training. This makes them highly adaptable and capable of handling a wide range of requests.
Use Case: A tech startup can leverage GPT-3’s zero-shot capabilities to quickly develop a range of AI tools, from data analysis to content creation, without the need for extensive training data.
Few-Shot Models:
Few-shot models are similar to zero-shot models but require a few examples to perform a new task. GPT-3 again serves as an example, where it can adapt to new tasks with just a few prompts.
Use Case: A legal firm could use GPT-3 to draft legal documents by providing a few examples of the desired output, saving time and resources on routine drafting tasks.
Fine-Tuned Models:
LLaMA (Large Language Model Meta AI) is an example of a fine-tuned model that has been further trained on specific datasets to perform specialized tasks. This is useful for applications that require a deep understanding of a particular field or dataset.
Use Case: A pharmaceutical company might use LLaMA to analyze scientific research papers, extracting relevant information to aid in drug discovery and development processes.
By integrating these LLMs into their operations, businesses can automate complex tasks, enhance customer experiences, and gain valuable insights from their data. The versatility and adaptability of LLMs make them a powerful tool for businesses looking to leverage the latest in AI technology.
The Evolution and Future of LLMs
LLMs have evolved from simple models that could predict the next word in a sentence to sophisticated systems capable of managing paragraphs and entire documents. As they continue to advance, they promise to further revolutionize the way we interact with technology, making it more intuitive and seamless.